Connect to Turbot Pipes from Jupyter Notebook
Since your Turbot Pipes workspace is just a Postgres database, you can use the
standard psycopg2 adapter to query your workspace database from Python.
You can get the information needed to connect to your Turbot Pipes database instance from the Developers tab on the Steampipe page for your workspace.

It's the usual drill: import psycopg2, specify your connection string, create a connection, then run a query. (See also: Connect to Turbot Pipes from Python.)
In this example we connect from an instance of Jupyter Notebook running in VSCode, load the query results into a
pandas.DataFrame, then use itsdescribemethod to summarize the data.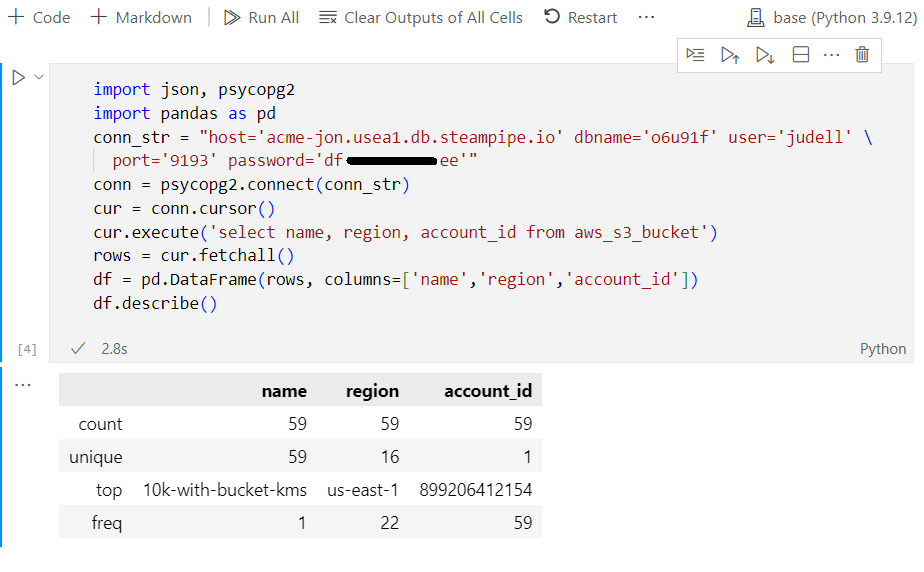
Connect to Steampipe CLI from Jupyter Notebook
To connect Jupyter Notebook to Steampipe CLI,
run steampipe service start --show-password and use the displayed connection
details.
Steampipe service is running:
Database:
Host(s): localhost, 127.0.0.1, 172.28.158.171 Port: 9193 Database: steampipe User: steampipe Password: 9a**-****-**7e Connection string: postgres://steampipe:9a49-42e2-a57e@localhost:9193/steampipeCall the Turbot Pipes API from Jupyter Notebook
You can also use the
Turbot Pipes query API.
Grab your token, put it an
environment variable like PIPES_TOKEN, and use this pattern.
import json, os, requestsurl = 'https://pipes.turbot.com/api/latest/org/acme/workspace/jon/query'data = {'sql':'select name, region from aws_s3_bucket limit 2'}token = os.environ['PIPES_TOKEN']headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer " + token}r = requests.post(url, headers=headers, data=data)print(json.dumps(r.json(),indent=4)){ "items": [ { "name": "10k-with-bucket-kms", "region": "us-east-2" }, { "name": "10k-with-standard-kms", "region": "us-east-2" } ]}