Guardrails
Guardrails
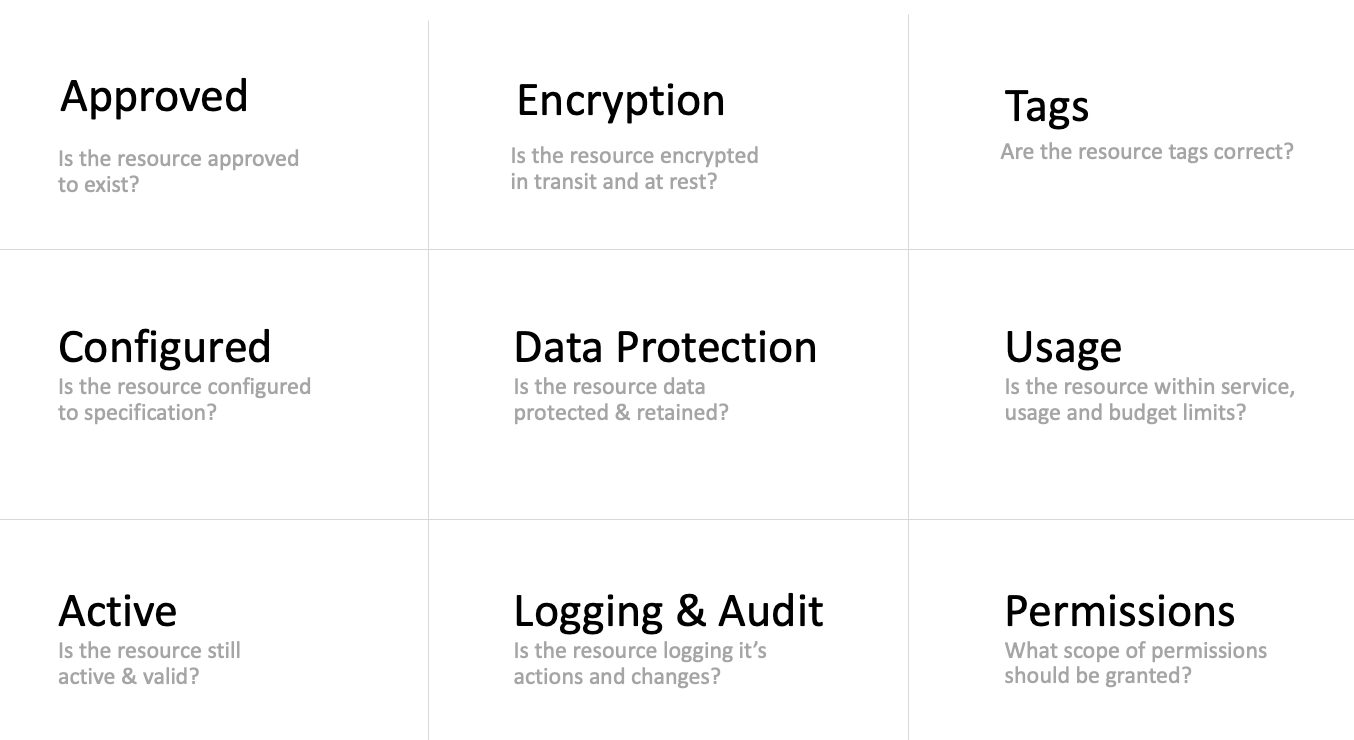
Turbot Guardrails Policies and Controls provide a flexible framework for auditing and enforcing configuration across hundreds of cloud services, networking, OS, and DB tiers. While this model is extensible, there are many guardrails that are common and consistent across resources.
| Guardrail | Description |
|---|---|
| Access Logging | Monitor and enable access logging on various cloud resources. |
| Active | Use a variety of criteria to determine if a cloud resource is Active, i.e. number of days the resource has existed, and take action (shutdown, delete, alarm, etc). |
| Approved | Verify whether a particular resource is allowed to exist and take an appropriate action if not (shutdown, delete, alarm, etc). |
| Audit Logging | Audit Logging configuration tools for cloud resources. |
| Budget | A mechanism for tracking current spend against a planned target and taking appropriate action to control cost. |
| CMDB | Responsible for populating and updating all the attributes for that resource type in the Guardrails CMDB. |
| Discovery | Mechanism by which Guardrails initially adds a resource to the CMDB. |
| Encryption at Rest | A mechanism to manage data encryption at rest (i.e. AWS S3 Buckets). |
| Encryption in Transit | A mechanism to manage data encryption in transit (i.e. AWS S3 Buckets). |
| Intelligent Assessment | AI-powered resource assessment to evaluate compliance using natural language. |
| Public Access | Configure public access settings on cloud resources. |
| Scheduling | Define schedules to control cloud resource usage. |
| Stacks/ Configured | [DEPRECATED] Manage resource configuration using Terraform. |
| Stacks [Native] | Manage resource configuration using OpenTofu (open source Terraform). |
| Tagging | Tagging of both Guardrails resources, such as a folder, and Cloud Provider resources, such as an Azure Subscription or AWS EC2 instance. |
| Trusted Access | Trusted Access allow you to define whom and what you trust and enforce those limitations on your cloud resources. |
| Usage | Generate alarms if the number of resources in a specific service exceeds a set amount. |