Guardrails Firehose for AWS SNS
The Guardrails Firehose generates an event stream of notification sent to an AWS SNS
topic. It is ideal for extracting event streams from Guardrails then sending them to
various consumers such as email, a Security Information and Event Management
(SIEM) tool, a logging tool, etc. The Firehose answers the question "Can I get a
stream of change events flowing through Guardrails?". It can't answer "How many
controls are in ok?" or "How many storage buckets are in the environment?"
Customers who need snapshots of the environment or bulk data extracts of
resources, control states or other data should use GraphQL or
Steampipe.
Event correlation would be handled by products that consume the Firehose event stream. Also, the Firehose is responsible for delivery of notifications to the Firehose SNS topic. Any integrations that subscribe to the Firehose topic are completely up to the customer. Only notifications created after Firehose configuration will be reprocessed. There is no way to force resending of notifications in a given time range.
How It Works
The Guardrails Firehose composes a number of stages for taking a notification event in Guardrails through to final delivery on an AWS SNS topic.
Notification generated by change on a resource, control, policy, etc -> Watch Filter selects notifications to send -> Render the Notification Template -> Publish to AWS SNS topic -> Downstream integrations- As resources, controls and policy settings change inside Guardrails, entries are added to the Notifications table.
- Watch filters select some subset of those notifications to be send to the Firehose.
- Notifications are passed through a Notification Template to prepare them for delivery to the Firehose.
- A background process takes rendered notifications then publishes them to the Firehose Topic.
Setup Guardrails Workspace and AWS Resources
The following steps cover how to manually install and configure the mod. If Terraform is preferred, use this mod example for steps 2 - 5 and creating the Guardrails Firehose.
- Install the mod into the workspace if not already installed. See Installing Mods for more guidance.
- Create the AWS SNS topic. It can be in any account and any region. All the notifications will be forwarded to this topic.
- Create an AWS IAM User with access to the above SNS topic. Guardrails will use
this user to publish to the SNS topic. Guardrails recommends having a specific
user that is only used for notification forwarding. The IAM policy on the
Firehose user should also be least-privilege with only
Publishpermissions to the Firehose SNS topic alone. - Generate an access key pair for the above IAM User.
- Set the following Guardrails policies. Note that these can ONLY be set at the
Turbot level:
Turbot > Firehose > AWS SNS > Notification Topic- This is the topic ARN from step 2.Turbot > Firehose > AWS SNS > Notification Access Key- This is the access key from step 4.Turbot > Firehose > AWS SNS > Notification Secret Key- This is the secret key from step 4.
- This completes the AWS configuration and Guardrails Workspace configuration. Watches must still be created for notifications to flow through the Firehose.
Setup Firehose Watches
A Guardrails Firehose watch specifies a set of parameters used to filter for which notifications to send. A watch consists of the following:
| Parameter | Description | Common Value |
|---|---|---|
| action | [REQUIRED] The action the Watch takes when it finds a match, either a Guardrails ID or URI. | tmod:@turbot/firehose-aws-sns#/action/types/router |
| favorite | [OPTIONAL] Favorite to associate the Watch with, as a Guardrails ID. | Varies by user |
| filter | [REQUIRED] A valid filter to determine which notifications to process. | Varies by use case |
| resource | [REQUIRED] The resource to create the Watch for, either a Guardrails ID or AKA. | Turbot resource ("tmod:@turbot/turbot#/"), Guardrails Folder, or Cloud resource |
The
Terraform docs
show how to set this information using Terraform. Generally, the filter
parameter is the most complex and has extensive coverage below.
Watch Filters
Watches specify the filter criteria for matching notifications. A matched notification will be sent through the Firehose pipeline. More information on notification filters can be found in the Notification Filters docs.
Supported Filter Pivots
| Keyword | Value | Example |
|---|---|---|
controlCategoryId | Guardrails ID or AKA of the Control Category. | controlCategoryId:'tmod:@turbot/turbot#/control/categories/cmdbDiscovery' |
controlCategoryLevel | level and / or descendant | controlCategoryLevel:self,descendant |
controlTypeId | Guardrails ID or AKA of the Control Type. | controlTypeId:'tmod:@turbot/aws-s3#/control/types/bucketVersioning' |
controlTypeLevel | level and / or descendant | controlTypeLevel:self,descendant |
level | level and / or descendant | level:self |
policyTypeId | Guardrails ID or AKA of the Policy Type | policyTypeId:'tmod:@turbot/aws-s3#/policy/types/bucketVersioning' |
policyTypeLevel | Guardrails ID or AKA of the Policy Type | policyTypeLevel:self,descendant |
resourceCategoryId | Guardrails ID or AKA of the Resource Category | resourceCategoryId:'tmod:@turbot/turbot#/resource/categories/storage' |
resourceCategoryLevel | level and / or descendant | resourceCategoryLevel:self,descendant |
resourceTypeId | Guardrails ID or AKA of the Resource Type | resourceTypeId:'tmod:@turbot/aws-s3#/resource/types/bucket' |
resourceTypeLevel | level and / or descendant | resourceTypeLevel:self |
notificationType | See Supported Notification Types | notificationType:active_grants_deleted |
Supported Notification Types
| Item | Action | Notification Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Action | Notify | action_notify | When a Guardrails action invokes a notify command during a run. |
| Control | Change | control | Aggregates both control_updated and control_notify notification types |
| Control | Notify | control_notify | When a Guardrails control invokes a notify command during a run. |
| Control | Updated | control_updated | When a Guardrails control is updated. Mainly, this is done to change the state of a control. |
| Favorite | Created | favorite_created | When a favorite is created for a resource. |
| Favorite | Deleted | favorite_deleted | When a favorite is deleted for a resource. |
| Grant Activation | Created | active_grants_created | When a Guardrails grant is activated. |
| Grant Activation | Deleted | active_grants_deleted | When a Guardrails grant is deleted. |
| Grant | Created | grant_created | When a Guardrails grant is created. By default in the UI "Activate for immediate use" is checked. In that case, a grant_created notification is generated followed by active_grants_created. |
| Grant | Deleted | grant_deleted | When a Guardrails grant is deleted. |
| Policy Setting | Created | policy_setting_created | When a new Guardrails policy setting is created. |
| Policy Setting | Deleted | policy_setting_deleted | When an existing Guardrails policy setting is deleted. |
| Policy Setting | Updated | policy_setting_updated | When an existing Guardrails policy setting is updated. |
| Policy Value | Updated | policy_value_updated | When a Guardrails policy value is updated. |
| Resource | Change | resource | Aggregates all resource_* notifications. |
| Resource | Created | resource_created | When a new resource is created in Guardrails. |
| Resource | Deleted | resource_deleted | When a resource in Guardrails is deleted. |
| Resource | Updated | resource_updated | When a resource in Guardrails is updated. |
Warnings and Notes on Watches
WARNING
- Creating other notifications beyond the supported notification types below will cause system instability.
NOTE
- Watches do not support specifying a
resourceIdin the filter. If you want to monitor a specific resource, create the watch on that resource instead. - Filtering by
control_updatednotifications by control state is not supported. All control state notifications will be delivered ifnotificationType:'control_updated'is specified.
Creating Filters for Watches Easily
Manually constructing Watch filter strings can be tedious and error-prone. Instead, Watch filters can be interactively prototyped using the "Activity Ledger" report in the Guardrails Console. Guardrails will also auto-generate the filter string.
- Go to the Reports tab in the Guardrails Console.
- Find the "Activity Ledger" report. Both the Firehose and Activity Ledger
report examine the
notificationstable, so whatever rows show up in the Activity Ledger will show up in the Firehose too. - Customize the report to provide exactly the desired information.
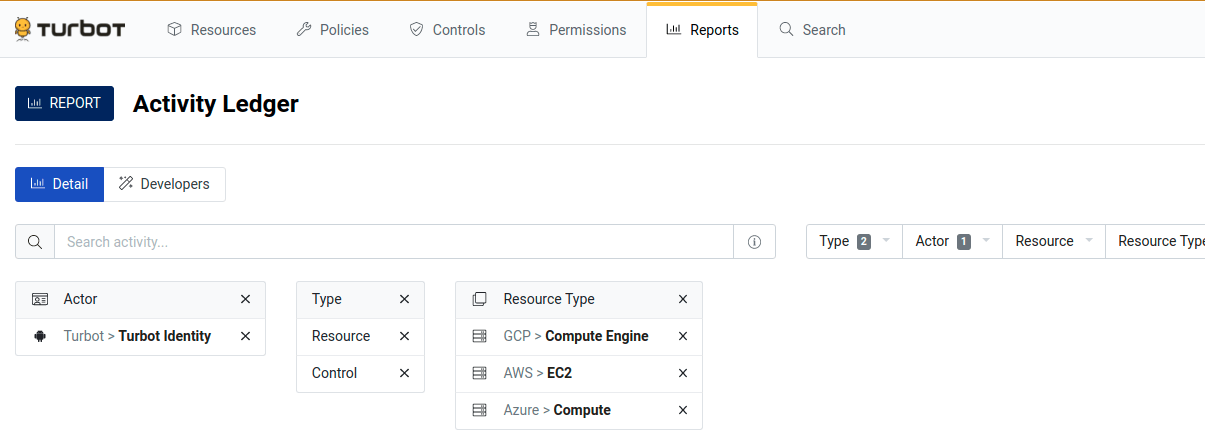
- Go to the little Developers tab on the reports page. Click on one of the
queries in the GraphQL section. This will take you to the main GraphiQL
console.
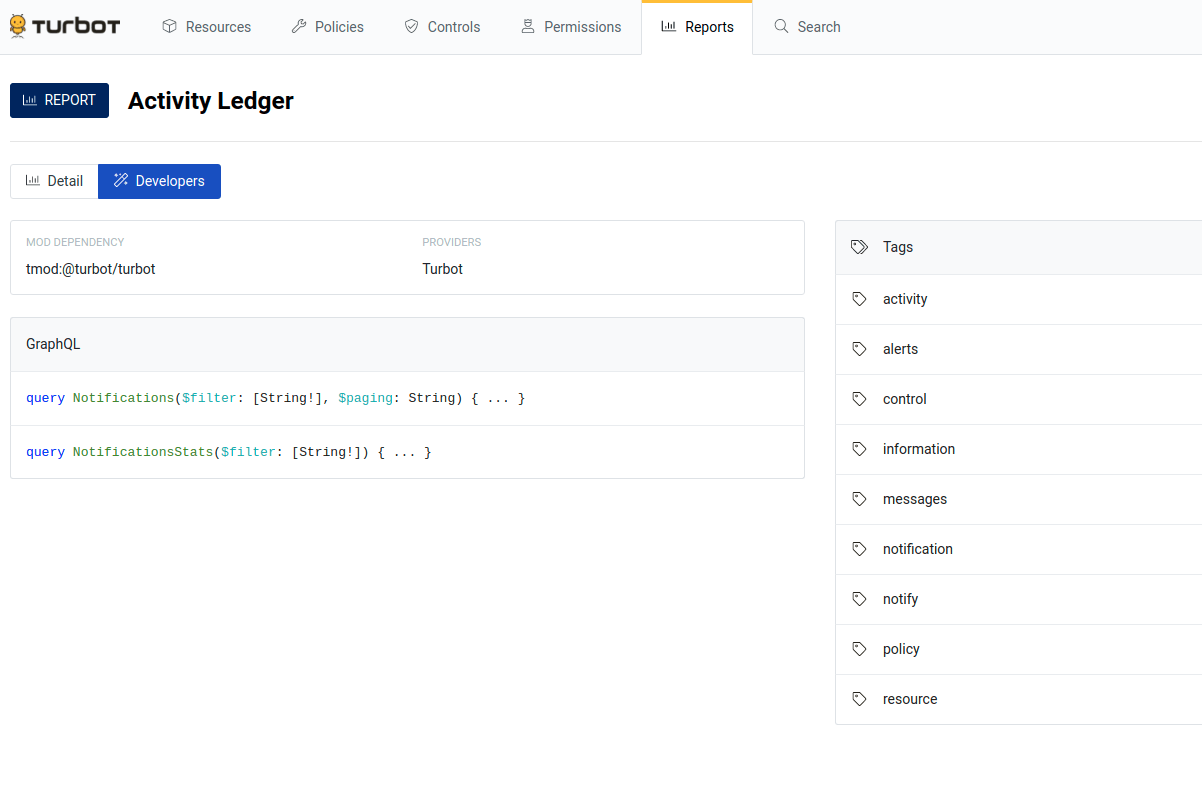
- In the bottom left, there’s a Query Variables section.
- The “filter” in the variable section is the machine generated filter that
matches your report.
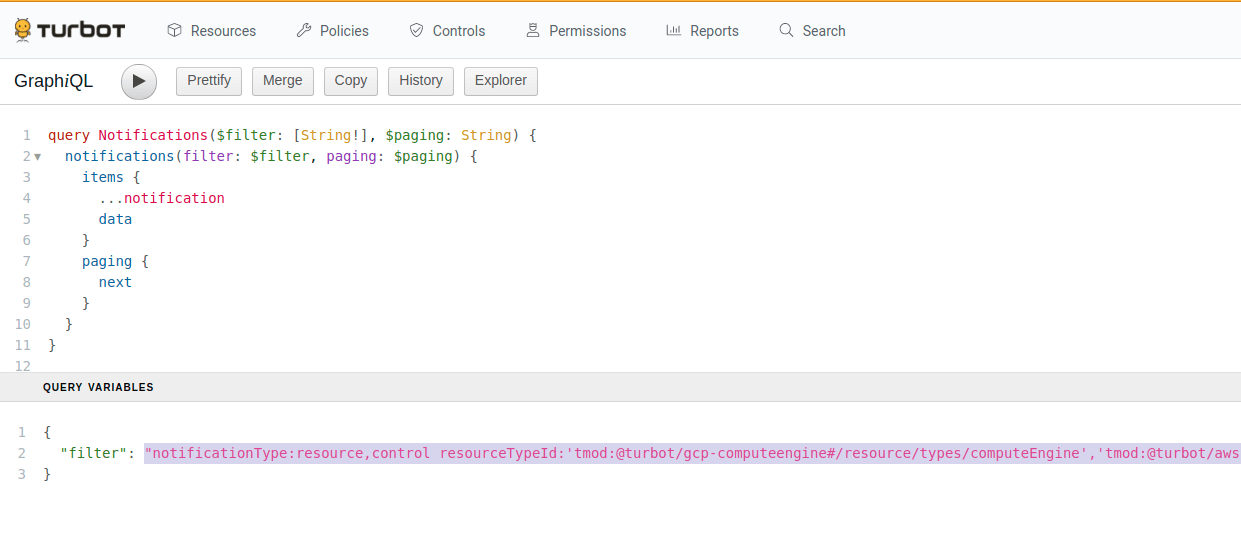
- Copy the filter string into your watch.
- Create the watch using the GraphQL queries in the next section.
This same process is used when building filter strings for Steampipe queries for the turbot_notification table.
When building a watch filter string using the Activity Report, Guardrails may
include the umbrella notification types resource and control. The resource
notification type aggregates resource_created, resource_updated and
resource_deleted. The control notification type aggregates the
control_notify and control_updated notification types. The umbrella
notification types are a good starting place but can be replaced if more
specificity is required.
There is an important difference between control_notify and control_updated.
Control Notify will tell you when a control has taken an action, typically to
remediate. Control Updated notifications record when a control has changed
state. Customers are typically more interested in the control_updated
notifications.
Common Filters
While the Firehose has a wide selection of
notification types, the most commonly used are
control_updated, resource_created, resource_updated and
resource_deleted. The below examples should serve as a starting point. Filters
for specific cloud accounts or services can be built using the
creating filters instructions above.
Controls
All AWS Control Updates for entire workspace:
notificationType:control_updated controlTypeId:'tmod:@turbot/aws#/resource/types/aws'All Azure Control Updates for entire workspace:
notificationType:control_updated controlTypeId:'tmod:@turbot/azure#/resource/types/azure'All GCP Control Updates for entire workspace:
notificationType:control_updated controlTypeId:'tmod:@turbot/gcp#/resource/types/gcp'All cloud platforms for entire workspace:
notificationType:control_updated controlTypeId:'tmod:@turbot/aws#/resource/types/aws','tmod:@turbot/azure#/resource/types/azure','tmod:@turbot/gcp#/resource/types/gcp'All AWS S3 Bucket Control Updates for entire workspace:
notificationType:control_updated controlTypeId:'tmod:@turbot/aws-s3#/resource/types/bucket'All Azure Storage Account Control Updates for entire workspace:
notificationType:control_updated controlTypeId:'tmod:@turbot/azure-storage#/resource/types/storageAccount'All GCP Bucket Control Updates for entire workspace:
notificationType:control_updated controlTypeId:'tmod:@turbot/gcp-storage#/resource/types/bucket'Encryption at Rest controls for all Cloud Platforms:
notificationType:control_updated controlCategoryId:'tmod:@turbot/turbot#/control/categories/resourceEncryptionAtRest'
Resources
- Resource Created:
notificationType:resource_created - Resource Updated:
notificationType:resource_updated - Resource Deleted:
notificationType:resource_deleted - All Resource Changes:
notificationType:resourceornotificationType:resource_create,resource_updated,resource_deleted
Creating Watches
Firehose watches can be created and managed using GraphQL or Terraform.
Create Watch by Terraform
Watches can be created by Terraform. The Terraform docs have more information.
resource "turbot_watch" "active_grants_deleted" { resource = "185423120545381" action = "tmod:@turbot/firehose-aws-sns#/action/types/router" filters = [ "level:self,descendant notificationType:active_grants_deleted" ]}Updating and deleting Watches using Terraform is done in the usual way. If a watch does not update with Terraform then destroy the watch and recreate it with the new filter string.
Create Watch by GraphQL
Create a watch using GraphQL:
mutation CreateWatch($input: CreateWatchInput!) { createWatch(input: $input) { filters handler turbot { id resourceId } }}GraphQL Input: Note that the resource field should be one of these: The Guardrails
resource, a Guardrails folder or a cloud resource. Attaching a watch to any other
type of resource (Guardrails control types, policy settings, etc) won't generate the
expected notifications.
{ "input": { "resource": "185423120545381", "action": "tmod:@turbot/firehose-aws-sns#/action/types/router", "filters": ["level:self,descendant notificationType:active_grants_deleted"] }}Upon successful watch creation, you will see a response like the below example:
{ "data": { "createWatch": { "filters": [ "resourceId:185423120545381 level:self,descendant notificationType:active_grants_deleted" ], "handler": { "action": "tmod:@turbot/firehose-aws-sns#/action/types/router" }, "turbot": { "id": "215276026059506", "resourceId": "185423120545381" } } }}Getting list of Watches
To get the list, use the following example.
query MyWatches { watches(filter: "") { items { handler filters watchRules { metadata { filters } } } }}Guardrails will return any watches:
{ "data": { "watches": { "items": [ { "handler": { "action": "tmod:@turbot/firehose-aws-sns#/action/types/router" }, "filters": [ "resourceId:185423120545381 level:self,descendant notificationType:active_grants_deleted" ], "watchRules": { "metadata": { "filters": [ "watchId:215276026059506" ] } } } ] } }}If there are no watches configured in the workspace, you'll see
{ "data": { "watches": { "items": [] } }}Deleting Watches
To delete a watch, use the following mutation example. Copy the long number from
watchId in $.data.watches.items[].watchRules.metadata.filters[].watchId from
the results of the MyWatches query.
mutation DeleteMyWatch { deleteWatch(input: { id: "215276026059506" }) { handler filters }}Upon successful deletion, you will see a similar response:
{ "data": { "deleteWatch": { "handler": { "action": "tmod:@turbot/firehose-aws-sns#/action/types/router" }, "filters": [ "resourceId:185423120545381 level:self,descendant notificationType:active_grants_deleted" ] } }}Running MyWatches again should show that the watch has been deleted.
Notifications
A Notification represents an event that occurred in Guardrails. The notification will include detailed information about the affected resource, control, policy value, policy setting, etc. This data includes the object detail before and after the event, standard Guardrails metadata, and other details of the event.
Sample Notification
Below is a sample notification of type active_grants_deleted.
{ "notificationType": "active_grants_deleted", "actor": { "identity": { "picture": "https://www.gravatar.com/avatar/cb9ff8606c24daf9cda1d82615bd7a8e", "turbot": { "title": "Timon Berkowitz", "id": "186957187212252" }, "title": "Timon Berkowitz" } }, "turbot": { "id": "202473982728085", "createTimestamp": "2020-09-10T17:34:58.063Z" }, "oldActiveGrant": { "grant": { "type": { "trunk": { "title": "Turbot" } }, "level": { "trunk": { "title": "User > Metadata > ReadOnly" } }, "resource": { "trunk": { "title": "Turbot" } }, "identity": { "trunk": { "title": "Turbot > Turbot Local > Pumbaa Smith" } } }, "resource": { "trunk": { "title": "Turbot" } } }}Notification Template
The "Render Template" pipeline action will execute the query and nunjucks
template in the Notification Template policy. The transformed notification will
then be placed on the Firehose SNS topic. These render templates are implemented
as Guardrails policies. You may choose to override these templates (policies) in the
format that is suitable for your need. For example, in order to update the
render template for active_grants_deleted notification type, use the Guardrails
Policy
Turbot > Firehose > AWS SNS > Notification Template > Active Grants Deleted.
All supported templates can be found under the parent policy type
Turbot > Firehose > AWS SNS > Notification Template > *.
Additional information can be added to the notification queries in the Notification templates. Use the GraphiQL Developers tab in the Guardrails console to test out altered notification queries.
The output of the notification template by default is JSON but can be in whatever format fits your needs best.
Notification templates cannot be made into calculated policies.
Troubleshooting
Sometimes a part of the Firehose data path breaks down. The questions below point to common points of missing or misconfiguration of the Firehose pipeline.
For reference, here's the data path again. Each one of these steps needs to operational for notifications to flow.
Notification generated (resource, control, policy, etc) -> Watch -> Render the Notification Template -> Publish to AWS SNS topic -> Downstream integrationsFirehose Mod and Policies
- Is the Guardrails Firehose mod installed and has no errors?
- Are all the firehose policies set up to known good values? Topic ARN, Access Key, Access Secret.
- If the Firehose was configured manually, have you configured all the same resources as created by the Firehose Terraform in the Guardrails Samples Repo?
Firehose Watches
- If notifications aren't coming through, set the watch to something as broad as possible and attached to the Guardrails resource; something like "get control_updated notifications for all {platform} controls for all {platform} resources in the workspace". This has the best chance to generate some traffic on the firehose topic. Such a broad scope for notification may be long-term undesirable but is very helpful for validating the Firehose data path. Watches can always be refined later.
- Does your watch filter have any typos in it? Developing a filter string using Creating Filters For Watches helps eliminate subtle typos and gives a preview of notifications the Firehose will deliver.
- Are the watches attached to the right resource? Make sure the watch is attached to either the Guardrails resource ('tmod:@turbot/turbot#/'), a folder or a cloud account.
- Does the watch filtering for the right kinds of notification?
- It's easy to generate
controls_updatedtraffic by switching a policy exception on a single resource fromCheck: EnabledtoCheck: Disabledand back again. Changing the resource works in the platform console works too.
Firehose Notification Templates
- Start with the default notification templates. Add conservatively from there.
- The notification query can be tested in the GraphiQL Developer's console in the top right corner of the Guardrails console. This is a great place to experiment with adding or removing parts from the notification query.
Firehose Topic and User
- Can you send messages to the Firehose topic using the AWS cli and the Firehose user credentials?
- As a troubleshooting measure only, enable success and failure delivery logging for the Firehose SNS topic. This can tell you if there are any problems with the SNS subscription. In high volume environments, keeping success delivery logging after initial configuration may be unnecessary.
- What are the firehose topic subscriptions? Sending to an SQS queue or to an email address are common subscription endpoints.
- For enterprise customers, do you see log entries in the
/aws/lambda/{turbot_prefix}_turbotfirehoseawssnssender-{hash}CloudWatch Logs? SaaS customers please work with Guardrails Customer Success to investigate Firehose problems. - Does the Firehose Topic policy allow the Firehose IAM user to publish to it? (No permissions beyond publish are required.)
- Do you have a plan for Access Key rotation?
Downstream Integrations
- There is some lag from when a notification is generated till it shows up on the firehose topic. A lag of 30 to 60 seconds is common; 5 minutes has been observed too. Delivery depends on overall system load.
- If there is additional routing that happens after the firehose SNS, does it work when messages are fed manually onto the Firehose topic?